Auto workshops can use Connected Car technologies to stay in touch with their customers and improve servicing outcomes. The article shall deep dive Into multiple ways workshops can leverage connected car technology. These include: increasing workshop utilisation by monitoring each customer’s car usage since the last service and using that to identify the right point to call in the vehicle for the next service. Offer proactive maintenance by remotely identifying if a car has any issues. Proactively get in touch with customers with the right advice and offers. Differentiate from the competition with a caring and personalised servicing experience for your customers.
Connected Car technology that enables real-time monitoring of vehicles and insights based on vehicle data is leading to newer business models and revenue generation opportunities for the entire auto ecosystem. Commonly referred to as telematics, we see growing worldwide adoption of telematics by various players in the ecosystem including automotive, after-market, mobility, logistics, and vehicle insurance.
Auto OEMs and Tier-1’s use on-road vehicle data gathered under varied driving conditions to improve designs, manage warranties and offer connected vehicle solutions to customers. Predictive maintenance models using telematics data help auto service networks offer optimised maintenance service for their customers. Auto insurance companies use telematics to develop underwriting models for usage based insurance policies. Logistics and mobility companies use telematics for fleet management, driver behaviour, and fuel monitoring and to improve the overall efficiency of their operations.
Connected vehicles generate a massive amount of data that presents a monetization and cost-saving opportunity. Car generated data may become a USD 450 – 750 bln market by 2030, as per McKinsey.
Auto workshops can use connected car technologies to stay in touch with their customers, improve servicing outcomes and differentiate from the competition.
Here we detail some of the key use cases of connected car technologies for auto workshops.
Guide Customer on when to Service a Vehicle
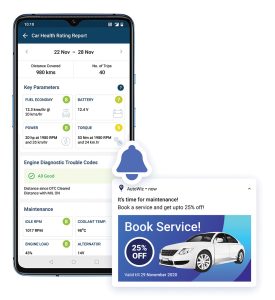
Currently, vehicle servicing is based on an OEM-prescribed preventive maintenance schedule or in case the vehicle has some kind of breakdown. Using connected car technologies, vehicle owners can monitor the true condition of their vehicle and be automatically advised to go for servicing when the need arises. For this either an OEM-fitted telematics device or an easy-to-install aftermarket OBD dongle can be used to provide a mobile app to the vehicle owner.
Such user-facing, feature-rich mobile app for customers keeps them engaged and loyal to your workshop – such apps typically include multiple features including live tracking, driving behaviour, fuel monitoring and car health. The app could include a comprehensive health report based on historical data and a comparison with a peer set of cars. This helps the end user rate the car on key performance and maintenance parameters and guides the customer on when to service the car.
For example, the App can measure the battery voltage and guide the customer on when might be the right time to replace the battery. The app can also show any engine diagnostic trouble code encountered and what could be the implication of that code. A diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is a code stored in a vehicle’s onboard diagnostic system (OBD) that indicates there is a problem with the vehicle’s emissions, engine, or transmission. These codes are used to help diagnose and troubleshoot issues with a vehicle and are generated when the vehicle’s ECU system detects a problem or fault. As an example, a clogged or dirty air filter might be leading to low fuel mileage. If the clogged filter is causing the engine to run lean (not enough fuel), the diagnostic code that may be generated could be P0171 (System too lean, Bank 1) or P0172 (System too rich, Bank 1).
There are thousands of such DTCs that encode any issue encountered in a specific module or component of a system. By using connected car technologies, the end car owner can be self-guided to understand the sub-system/component to which the issue belongs. Based on the severity, the end user can be guided to get in touch with the workshop.
Connected Service Partner Portal Identifies Each Car’s Servicing Need
While the car owner can monitor their vehicle in the app, the workshop can monitor the car condition data for its affiliated vehicles in the service partner portal.
Via the service partner portal, workshops can monitor each car’s usage since the last service and get real-time alerts for battery, coolant and engine issues. To protect the privacy of the car owner, location-related data need not be visible to the workshop. However, relevant information relating to the usage, fuel economy, and other car vitals can be relayed to the service portal.
Using this information, workshop personnel can Identify the right point to call a particular customer for service. The information can be used to proactively get in touch with customers with the right advice and offer.
For workshop, this can help increase the utilisation of the workshop and also increase the number of relevant touch-points with the car owners.
OBD Based Car Inspection Solution in Workshop
Once the vehicle is in workshop for servicing or repair, connected car technologies can be used for better inspection and diagnosis of the vehicle.
Typically, workshops use a scanner to check the vehicle for any diagnostic trouble codes and diagnose and fix issues based on that. While these scanners are obviously useful, they typically don’t have any connectivity to the server or the cloud. Hence the technician needs to monitor and debug the issue with the car in the workshop.

enabled via connected car technologies
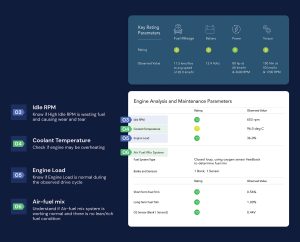
Using connected car technologies and OBD-based telematics, workshops can make this process more dynamic. With an OBD dongle connected to the cloud, the workshop mechanic can take a test drive on any incoming car into the workshop and generate a full inspection report. Such Inspection Report provides data-driven insights and ratings on the car’s internal condition including diagnostics, power, performance, and key maintenance parameters.
Since the connected car server is collecting data from thousands of cars, it can provide a better data-driven rating of each car by benchmarking it against the data from other cars with the same make, model, and year of manufacturing variant.
Post the completion of the servicing job, technician can again take a test drive and generate a post-service inspection report. Comparing the pre-and post-inspection report can indicate the impact of the specific improvements carried out during the servicing. This can give more credibility and confidence to the end customer regarding the servicing job carried out.
Over a period of time, workshops can also analyse patterns of diagnostic data across the population of their vehicles to predict warranty events and forecast inventory of spares in a particular region or a particular make. This can reduce warranty costs and Spare inventory to be maintained.
Grow Profitable Servicing Business with Connected Car Technology
The above are some of the key use cases enabled by connected car technologies for workshops. Workshop utilisation can be increased by monitoring each customer’s car usage since last service and using that to identify the right point to call in the vehicle for the next service. Workshops can offer proactive maintenance by remotely identifying if a car has any issues and getting in touch with customers with the right advice and offers.
Apart from increasing revenues and profits, the workshops can differentiate from the competition with a caring and personalised servicing experience for their customers.
Author
Co-founder and CEO
SenSight Technologies Private Limited (AutoWiz)

















































 KAMAL AGGARWAL
KAMAL AGGARWAL









